
The Impact of Poverty on Black Students’ School Attainment
Poverty is a complex issue with far-reaching consequences, and its impact on education is particularly concerning. Black students in the UK are disproportionately affected by poverty, which can have a significant negative impact on their school attainment. This article explores the relationship between poverty and educational outcomes for Black students, drawing on data and real-world examples to illustrate the challenges they face.
The Wealth Gap and Educational Disparity
The wealth gap between Black households and other demographics in the UK is a well-documented phenomenon. According to the Office for National Statistics (ONS), Black households have the lowest median household income, while White British households have the highest. In a 2022 article, The Guardian revealed that “More than half of UK’s Black children live in poverty”1.

This disparity is exacerbated by factors such as unemployment, underemployment, and limited access to financial services.The link between wealth and educational attainment is well-established. Students from low-income families often face significant challenges that can hinder their academic success.
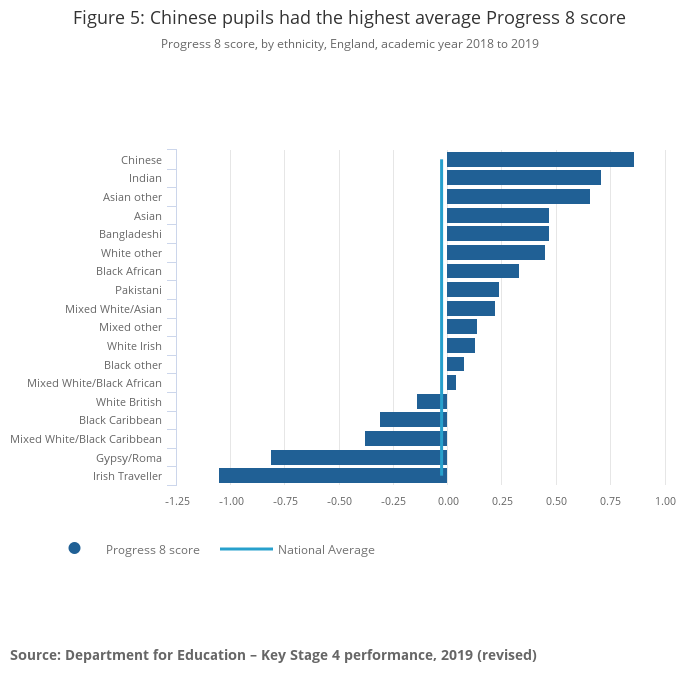
These challenges may include:
• Limited access to educational resources:
Students from low-income families may have limited access to books, computers, and other educational resources that are essential for learning.
• Poor housing conditions:
Inadequate housing can create a stressful and unhealthy environment for children, making it difficult to concentrate on their studies. The last Census shows that Black people are three times likely to live in social housing as their white peers (source : Office for National Statistics).
• Nutritional deficiencies:
Malnutrition can negatively impact cognitive development and academic performance. Programmes like “Healthy Starts”2 a scheme introduced by the NHS to provide nutritional safety net for pregnant women on low income tried to address this issue.
• Parental stress and involvement:
Parents who are struggling financially may be unable to provide the support and encouragement that their children need to succeed in school. Additionally, the data shows that Black women are more involved in the workforce than Black men compare to other ethnic group, making it harder to cope with homework follow up and stressful.

The Grenfell Tower Fire: A Tragic Example of Material Deprivation
The Grenfell Tower fire in 2017 highlighted the devastating consequences of material deprivation in the UK. The tower block, which was home to many low-income families, was destroyed in a fire that claimed the lives of 72 people (85% were from BAME community). The tragedy exposed systemic failures in housing regulations and exposed the vulnerability of marginalized communities to the effects of poverty.The Grenfell Tower fire had a profound impact on the lives of the survivors, many of whom were Black families. The loss of their homes and loved ones caused immense trauma and stress, which could have had a negative impact on their children’s education. Additionally, the survivors faced the challenges of finding new housing, rebuilding their lives, and providing for their families, all of which can be overwhelming and stressful.
Addressing the Impact of Poverty on Black Students’ School Attainment
Addressing the impact of poverty on Black students’ school attainment requires a multifaceted approach. Schools, policymakers, and communities must work together to create a more equitable and supportive environment for all students.
Some strategies that can be implemented include:
• Investing in early childhood education:
High-quality early childhood education can help close the achievement gap by providing children from disadvantaged backgrounds with the skills and support they need to succeed.
• Providing additional resources and support:
Schools should ensure that all students have access to the resources and support they need to succeed, regardless of their socioeconomic background. This may include tutoring, counseling, and after-school programs.
• Addressing systemic inequalities:
Policymakers must address the underlying causes of poverty, such as inequality in housing, employment, and education. This may involve implementing policies that promote social mobility and reduce economic disparities.
• Raising awareness and advocacy:
It is important to raise awareness of the challenges faced by Black students and advocate for policies that address these challenges.
By working together, we can create a more equitable and supportive environment for Black students and help them achieve their full potential.
Leave a comment